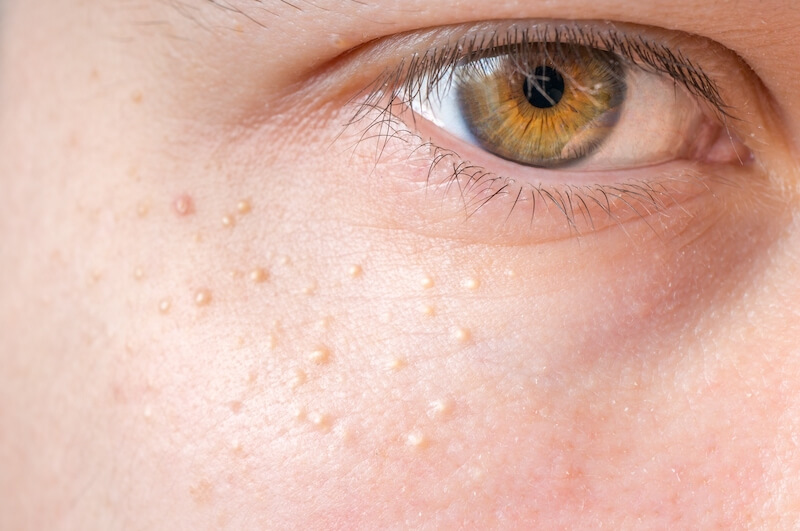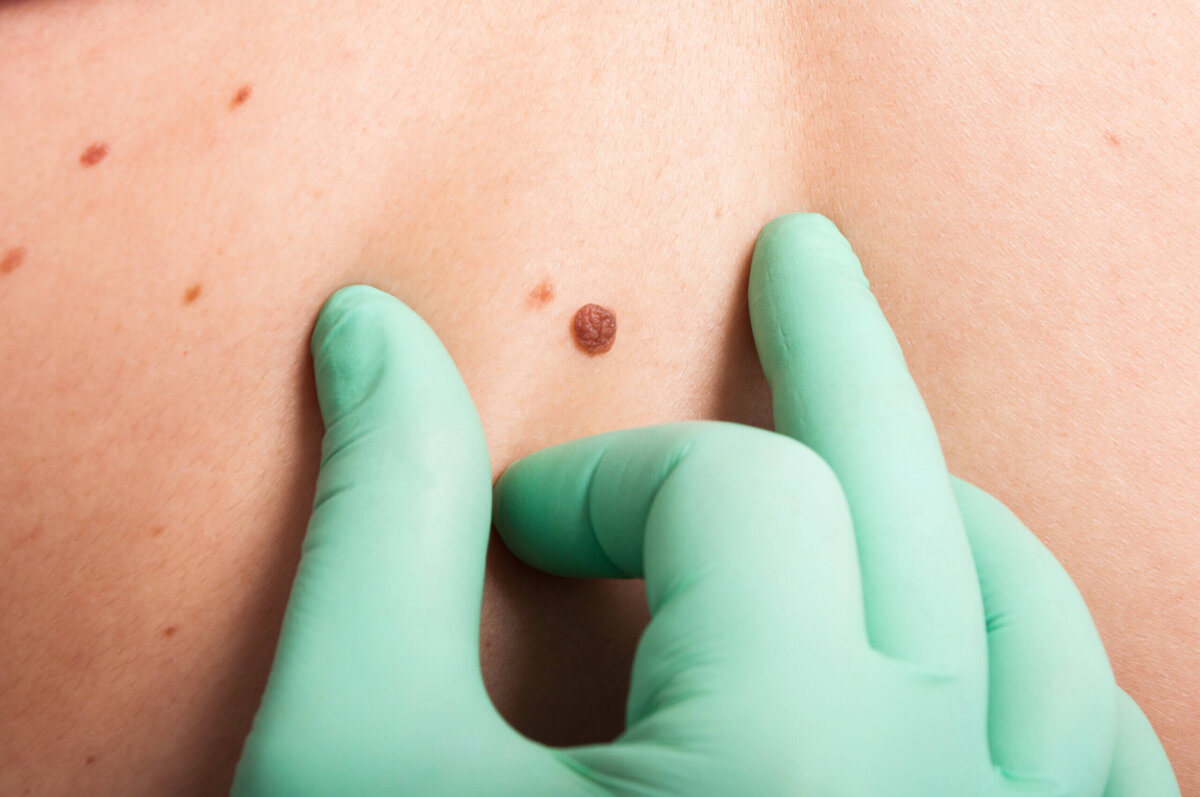
Mole Removal
Mole removal surgery depends on factors such as the type of mole, the size of the mole, and the location of the mole.
Mole removal is undertaken for a variety of reasons such as to establish a diagnosis, remove a changing mole or for cosmetic purpose.
- Professional | Established | Trusted
- Consultation and Assessment
- Various Treatment Options
- From $380 onwards


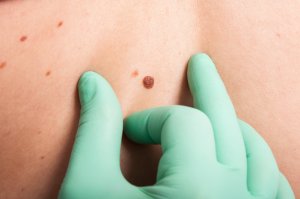
What is a Mole?
A mole is a collection of special pigment producing cells called melanocytes. There are generally two types of moles you can get. The most common (acquired) moles start appearing during or even before puberty. In about 1-2% of the population, (congenital) moles are present from birth.
Moles can change in appearance over time, and with puberty and pregnancy. It is important to monitor your moles for recent changes and see a doctor if your moles appear suspicious.
What are the types of moles?
Moles can take on different shapes and sizes, and may change with puberty, pregnancy and age.
Moles may appear at anybody site, and can take on different colours such as brown, black, blue or skin colour. They can appear flat, and may protrude from the skin (which is common on the face).
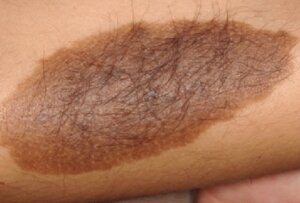
The acquired moles can range from a few millimetres in diameter to giant hairy congenital moles more than 20cm diameter seen in a newborn.
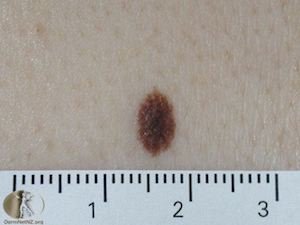
A junctional naevus, also known as an intradermal naevus, is a common type of mole (naevus) that develops at the junction between the epidermis (the outermost layer of the skin) and the dermis (the layer of skin beneath the epidermis). Junctional naevi typically arise from melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells of the skin, which cluster at the junction of these two skin layers.
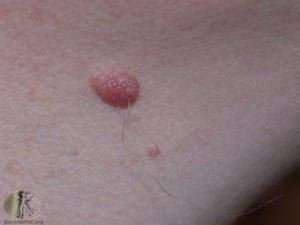
A compound naevus, also known as a junctional-compound naevus, is a type of mole (naevus) that displays characteristics of both junctional naevi and dermal naevi. It is formed by a combination of melanocytes located at the junction of the epidermis (the outer layer of skin) and the dermis (the deeper layer of skin) as well as within the dermis itself.
A congenital naevus, also known as a congenital melanocytic naevus or a congenital mole, is a type of mole that is present at birth or appears shortly thereafter. These naevi are caused by an overgrowth of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells of the skin, and are typically larger and darker than acquired moles that develop later in life.
A halo naevus, also known as a “halo mole” or “leukoderma acquisitum centrifugum,” is a type of mole (naevus) characterized by a surrounding area of depigmentation or lightening of the skin. The name “halo naevus” comes from the halo-like ring of lighter skin that encircles the mole. These moles are typically brown or black in color and may have a diameter ranging from a few millimeters to over a centimeter. It is most commonly found on the back.
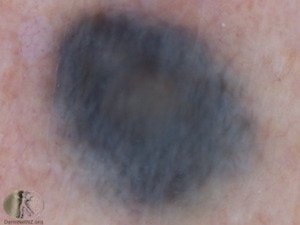
A blue naevus, also known as a “blue mole,” is a type of benign skin lesion that appears as a blue or blue-black pigmented spot on the skin. These lesions are typically composed of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells of the skin, and can occur anywhere on the body. Blue naevi are usually small, ranging in size from a few millimeters to a centimeter or more in diameter.
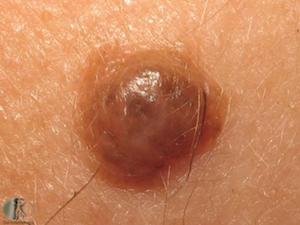
A Spitz naevus, also known as a Spitzoid melanocytic nevus or Spitzoid tumor, is a type of benign skin lesion that typically occurs in children and young adults. It was first described by Dr. Sophie Spitz in 1948. Spitz naevi are characterized by their distinctive appearance and can sometimes be difficult to distinguish from melanoma, a type of skin cancer.
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer, and accounts for the majority of deaths arising from all types of skin cancer. Melanoma has the highest incidence in Australia, New Zealand and North America.
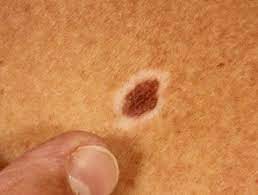
Following this easy to use ABCDE algorithm, any recent change in your mole warrants a visit to a doctor.
- Asymmetry of shape or colour
- Border irregular
- Colour variability (More than 3 colours)
- Diameter greater than 6mm
- Evolution or change over time

How are Moles diagnosed?
Moles are usually diagnosed based on their clinical appearance and their history of development.
In cases, where diagnosis is uncertain, we use a Dermatoscope, a specialised instrument to examine the mole under polarised light and magnification to better characterise the mole.
Moles that remain suspicious, or have recently changed are sent for a biopsy.

Why Mole Removal Surgery?
Although most moles can be left alone, you may wish to remove the mole for the following reasons:
- Unusual moles that are growing and you or your doctor may want a diagnosis to rule out cancer
- Moles that are inconveniently located, causing abrasions and skin irritation.
- Cosmetic purposes: Some may just not like the way it looks and want it removed.
Mole Removal Surgery - Procedures
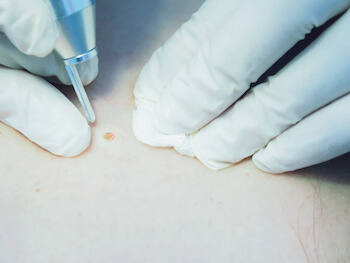
The majority of moles can be safely left alone after examination, and no further treatment is required.
You may wish to remove your moles if you are concerned of a recent change in your mole, the mole causes skin irritation or for cosmetic purposes.
The mole removal surgery method depends on the size, type of mole, your skin type and whether a biopsy needs to be done.
Mole removal surgery treatment options:
- Excision biopsy
- Shave biopsy
- Electrosurgery
- CO2 Laser mole removal
Frequently Asked Questions About Mole Removal
Mole removal surgery is performed under local anaesthetic. The procedure is virtually painless.
As with most surgical procedures, there is a risk of bleeding, infection, hyperpigmentation, hypopigmentation, scarring and recurrence.
Small moles usually recover within 7-10 days. For larger moles that require excision, it may take 10-14 days for the removal of stitches.
It is important to keep the wound clean after the mole removal procedure. Regular change of dressings and anti-septic cleansing will reduce the chance of infection. Avoid sun exposure to reduce chance of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and mole recurrence.
Yes, this can happen in some cases. This may be due to factors such as genetic susceptibility, age, location and type of mole. If a mole does recur, your doctor will advise you on the next appropriate course of action.
Mole removal surgery is from $360 onwards. The number of mole, size and depth of your mole and complexity of the procedure will determine the final cost of the procedure. Please speak to your doctor during your consultation.
schedule a consultation for mole removal in singapore
Do you have moles you are concerned about or wished to have removed? Contact us today to schedule a consultation, so Dr. Ng can develop a personalized treatment approach for resolving your skin concerns and helping you to achieve long-term improvements in the health and appearance of your skin.
Request a CallBack
Get in touch with us with any questions, pricing, or bookings.
Or give us a call at +65 6769 6007 | WhatsApp us +65 9855 3022
Related Information:
References:
- Zalaudek I, Schmid K, Marghoob AA, et al. Frequency of dermoscopic nevus subtypes by age and body site: a cross-sectional study. Arch Dermatol. 2011 Jun. 147(6):663-70.
- Haenssle HA, Mograby N, Ngassa A, Buhl T, Emmert S, Schön MP, et al. Association of Patient Risk Factors and Frequency of Nevus-Associated Cutaneous Melanomas. JAMA Dermatol. 2015 Nov 4. 1-8.
- Sardana, K., Chakravarty, P., & Goel, K. (2014). Optimal management of common acquired melanocytic nevi (moles): current perspectives. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 7, 89–103. https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S57782